- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Large Volume Injections›
- Ringer Solution
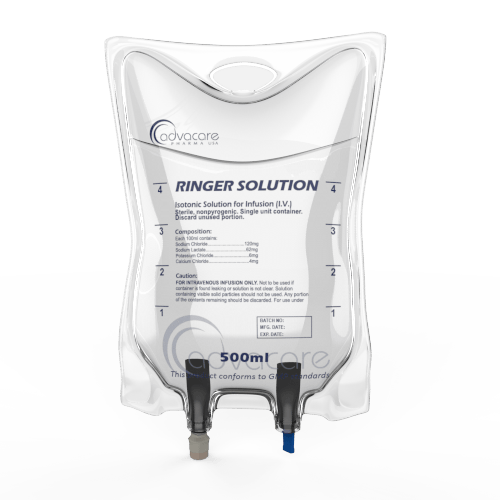
Ringer Solution
Dosage
Packaging
What is Ringer Solution?
Active Ingredients: Sodium Chloride, Potassium Chloride, Calcium Chloride Dihydrate
Ringer Solution is an isotonic solution used to quickly replace water and electrolytes in patients with low blood volume (hypovolemia) or low blood pressure (hypotension). This solution is a mixture of several salts: sodium chloride, potassium chloride and calcium chloride dihydrate.
This solution has been manufactured as a sterile, single-dose container for intravenous administration.
AdvaCare Pharma is a trusted global exporter of Ringer Solution. This medication is produced in our GMP-certified facilities in China, India, and the USA. Our manufacturing facilities are regularly inspected to ensure they comply with WHO standards, rules, and regulations.
Why are we a quality Ringer Solution manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma is a leading manufacturer of Ringer Solution Injection. For 20 years, we have been in the business of manufacturing GMP-approved high-quality, affordable pharmaceutical injection products to improve healthcare worldwide. Our control of the supply chain is data-driven and methodical, supported by highly skilled teams of professionals.
As a large-scale Ringer Solution manufacturer, we supply pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies and other medical organizations in more than 65 countries.
Uses
What is Ringer Solution used for?
It is used to replace water and electrolytes in patients with low blood volume or low blood pressure.
How should Ringer Solution be used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution, which should only be administered by a doctor or healthcare provider.
What dose should be given?
Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on dosage. Do not exceed what they advise.
Can patients with renal impairment take Ringer Solution?
The administration of Ringer’s Injection to patients with severe renal impairment or those at risk of such impairment may lead to the development of hyperkalemia or fluid overload. It is advisable to avoid using Ringer’s Injection in patients with severe renal impairment or conditions that could potentially cause sodium and/or potassium retention, fluid overload, or edema. In cases where the use of Ringer’s Injection cannot be avoided in patients with severe renal impairment, careful monitoring for the development of adverse reactions such as hyperkalemia, fluid overload, or edema is recommended.
Can patients with hepatic impairment take Ringer Solution?
In patients with severe hepatic impairment, there may be impaired lactate metabolism, and the administration of Ringer’s Injection may not lead to alkalization as expected. It is important to consider this factor when monitoring serum lactate levels in these patients. Monitoring lactate levels is crucial in individuals with severe hepatic impairment.
Can Ringer Solution be used during pregnancy?
No animal reproduction studies have been conducted with this solution. It is unknown if this injection can lead to fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. It is also unknown if this injection can affect the reproduction capacity. In pregnant women, this injection should be added only when clearly needed. If the woman develops a hypersensitivity reaction, the administration of Ringer should be limited. Also, this solution should be administered with caution during labor and delivery.
Can Ringer Solution be used during breastfeeding?
It is unknown if Ringer’s Solution is excreted in human milk. However, because many drugs are excreted in human milk, this injection should be administered with caution.
Can Ringer Solution be used in pediatric patients?
The safety and effectiveness of Ringer’s Injection in pediatric patients have not been established through adequate and well-controlled trials. However, the use of electrolyte solutions in the pediatric population is mentioned in the medical literature. It is important to note that the warnings, precautions, and adverse reactions identified on the label should be observed in the pediatric population.
When administering a lactate-containing intravenous solution to infants, consideration should be given to the fact that the liver and kidneys are still maturing during the first year of life. This maturation process can impact the biotransformation and renal excretion of lactate.
Pediatric patients are at an increased risk of developing hyponatremia, as well as the potential for developing encephalopathy as a complication of hyponatremia. Caution and close monitoring are advised when using Ringer’s Injection in the pediatric population.
Can Ringer Solution be used in geriatric patients?
Geriatric patients are at an elevated risk of developing electrolyte imbalances. Ringer's Injection is substantially excreted by the kidneys, and the likelihood of toxic reactions to this drug may be higher in patients with impaired renal function. Therefore, when prescribing for elderly patients, dose selection should be approached cautiously, typically starting at the lower end of the dosing range. This cautious approach reflects the higher prevalence of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function. Concomitant diseases or other drug therapies in the geriatric population can lead to side effects due to the Ringer Solution. It is advisable to consider monitoring renal function in elderly patients to ensure their safety and well-being during treatment with Ringer Solution.
What happens in cases of Ringer Solution overdose?
Overdose of Ringer Solution can lead to the following:
- fluid overload (pulmonary or peripheral edema)
- hyperkalemia or hypernatremia
- bicarbonate loss with an acidifying effect
- hypercalcemia
- metabolic alkalosis with or without hypokalemia
The effects of overdose need immediate medical attention and treatment. This condition should be treated with discontinuation of the injection, dose reduction, and monitoring of the fluid balance.
Other warnings
In cases of severe potassium deficiency, the potassium concentration from the Ringer Injection does not provide an efficient effect.
If the patient develops some adverse hypersensitivity reactions, the infusion should be stopped immediately. Appropriate therapeutic countermeasures must be instituted.
Hyponatremia might occur during Ringer administration, with the main symptoms of headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, and vomiting. Patients with brain edema are at increased risk of brain injury. The risk of hyponatremia is increased in patients with pulmonary failure and patients with non-osmotic vasopressin release. Hyponatremia is also a big risk for pediatric and older patients, as well as postoperative patients and patients with psychogenic polydipsia. Premenopausal women are also at risk of hyponatremia.
This solution might also lead to electrolyte disturbances like overhydration, congested states, pulmonary congestion, and edema. The fluid balance should be monitored, and doctors also need to evaluate the electrolyte concentrations and the acid-base balance.
Hyperkalemia might also occur because this solution contains potassium. Prone to hyperkalemia are patients with severe renal impairment, tissue injuries, acute dehydration, and cardiac disorders.
Administration of Ringer infusions can lead to metabolic alkalosis.
Hyperglycemia is possible in patients with impaired glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus.
The serum lactate levels need to be monitored in patients with metabolic acidosis.
During the administration of Ringer, Digoxin should be avoided because it might lead to a serious or fatal cardiac arrhythmia. Patients treated with thiazide diuretics and vitamin D also have an increased risk of hypercalcemia.
Drugs associated with sodium and fluid retention have an increased risk of hypernatremia and volume overload. Corticosteroids and corticotropin should be avoided, and the serum electrolyte status should be monitored.
Some antiepileptic and psychotropic medications might lead to adverse effects during the administration of Ringer Infusion. These drugs can reduce renal electrolyte-free water excretion, and patients are at increased risk of hyponatremia.
Ceftriaxone should not be administered concurrently with Ringer's infusion due to the risk of forming insoluble complexes with calcium, leading to potentially severe complications.
The renal sodium and lithium clearance is increased during the administration of Ringer Infusion, which results in decreased lithium concentrations.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Ringer Solution.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- swelling of the hands/ankles/feet
- trouble breathing
- muscle cramps/weakness
Hypersensitivity reactions due to Ringer administration may include the following:
- angioedema
- chest pain and chest discomfort
- decreased heart rate and blood pressure
- tachycardia
- respiratory distress and bronchospasm
- dyspnea, throat irritation, and cough
- urticaria, rash, pruritus, and erythema
- flushing
- paresthesias and hypoesthesia oral
- dysgeusia
- headache, nausea, anxiety, and pyrexia
- laryngeal edema and sneezing
- infection at the site of injection
- extravasation
- infusion site anesthesia (numbness)
Some common adverse effects due to metabolism and nutrition disorders include hyponatremia, hyperkalemia and hypervolemia.
General disorders at the administration site include the following conditions: phlebitis, infusion site inflammation, infusion site erythema, infusion site pain, infusion site swelling, infusion site pruritus, infusion site burning, and infusion site rash. A nervous system disorder that might occur very rarely is hyponatremic encephalopathy.
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor immediately.
Precautions
Do NOT use Ringer Solution if:
- You are hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
- You have hypervolemia.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.
This isotonic solution should not be used in newborns younger than 28 days who receive concomitant treatment with ceftriaxone. It is also not indicated for older patients, including adults who receive ceftriaxone in the same infusion line.
Patients with known hypersensitivity to sodium lactate should not use this solution.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions.
References
The Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer’s Solution in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study
This study evaluates the efficacy of Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer's solution in clinical practice. This retrospective cohort study included critically ill adult patients in intensive care for a period of 14 months.
It included 662 patients and this study revealed that compared to saline, Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer's solution had a better efficacy in critically ill patients.
The conclusion of this study is that Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer's solution has a potential protective renal function protective effect and causes no major alteration in arterial blood gas and plasma biochemistry.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.