- Home›
- Veterinary Pharmaceuticals›
- Veterinary Injections›
- Veterinary Liquid Injections›
- Thiamine HCl Injection
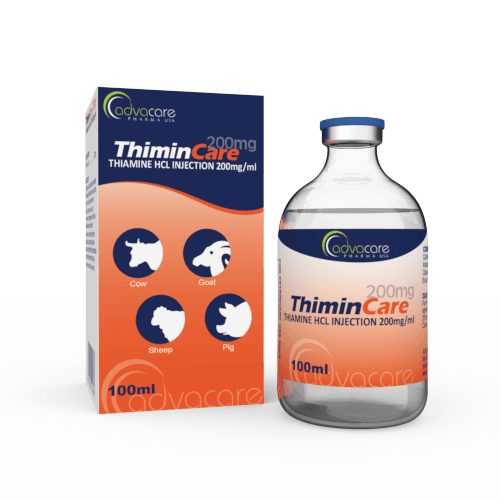
Thiamine HCl Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Thiamine HCl?
Active Ingredients: Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine HCl Injection is a parenteral supplement used to treat or prevent thiamine deficiency in dogs, cats, and horses. Balanced nutrition is very hard to achieve in animals, so this is a good supplementation in case of severe deficiencies. Some symptoms of thiamine deficiency include anorexia, excessive salivation, vomiting, coprophagy, tachyarrhythmia, and neuromuscular changes such as ataxia, seizures, muscle weakness, opisthotonus, or loss of reflexes.
Thiamine deficiency may be caused by poor diet or illness. Uncooked meat that contains sulfur dioxide (SO2) as a preservative can cause thiamine deficiency. Thiamine is also used for the adjunctive treatment of lead poisoning and ethylene glycol toxicity. It is also indicated for cerebrocortical necrosis and bracken poisoning.
Thiamine is a water-soluble vitamin known as vitamin B1. It is found naturally in foods like whole grains, brewer’s yeast, legumes, meat, milk, and cereals. This vitamin is needed to break down carbohydrates in the body.
It is important to note that Thiamine HCl Injection is for veterinary purposes only. In most countries, this drug should be used and applied by veterinarians.
This supplement is also available in tablets, which consists of a very complex composition, including vitamin A, vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B12, vitamin C, vitamin D3, manganese methionine, copper glycine, zinc methionine, iron glycine, chicken liver powder, microcrystalline cellulose, and silicon dioxide. This form of supplement can be used and given by both owners and veterinarians, and the usage is not limited only to veterinarians. There is also a similar multivitamin premix feed that can support the animal's overall health.
Thiamine HCl Injection is produced in our GMP-certified facilities located in China, India, and the USA. Our factories are routinely inspected to ensure they meet the high standards necessary to comply with WHO rules and regulations. AdvaCare Pharma is proud to offer a wide range of high-quality and cost-effective medical supplies that are available for distribution.
Why are we a trusted Thiamine manufacturer?
Thiamine Injection is manufactured and globally distributed by AdvaCare Pharma, a leading manufacturer of veterinary injections in the pharmaceutical industry. We have been committed to distributing high-quality, GMP-certified veterinary medications for the global market over the past 20 years. As a top Thiamine manufacturer, we ensure that all of our 100+ veterinary injections surpass our distributors' requirements by conducting routine internal and third-party facility audits.
Uses
What is Thiamine used for?
It is used to treat or prevent thiamine deficiency. It's also used to treat:
- lead poisoning
- ethylene glycol toxicity
- cerebrocortical necrosis
- bracken poisoning
What animals can be treated with Thiamine Injection?
It's recommended for cats, dogs, and horses.
What is the most common reason for Thiamine Hydrochloride administration in animals?
It is most commonly used to prevent:
- Thiamine deficiency in dogs and cats
- Thiamine deficiency-induced polioencephalomalacia (PEM) of sheep and cattle
In dogs and cats, thiamine deficiency occurs after an incomplete and unbalanced diet because thiamine is a normal dietary requirement in mammals. Thiamine deficiency is divided into three progressive stages:
- Induction stage
- Critical stage
- Terminal stage
The treatment process will depend on the stage.
The characteristics of the induction stage are vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia. If not treated with thiamine, the animal enters the critical stage with signs of ataxia, nystagmus, delayed pupillary response, blindness, paraparesis, and poor proprioception. Cats might show signs of cervical ventroflexion and dyspnea. Cardiovascular signs such as arrhythmias and bradycardia are also common in this stage.
Most cases of thiamine deficiency are diagnosed in the terminal stage and require immediate treatment with thiamine hydrochloride.
If thiamine is not normally produced by the bacteria in the cattle's rumen, it can lead to a brain degeneration called polioencephalomalacia or PEM. Thiamine in the rumen can be broken down by thiaminases and this can lead to thiamine deficiency in cattle. It reduces the energy of the brain and leads to polioencephalomalacia. The signs are agitation, anxiety, muscle twitching, abnormal head position, blindness, head pressing, lying down, seizure, and paddling.
Animals with PEM need an injection of thiamine three times a day for up to five days. This treatment focuses only on treating the deficiency. Thiamine injections are recommended in locations of PEM outbreaks.
How is a Thiamine Injection used?
This medication has been manufactured as a liquid, which is packaged in a vial. It is intended to be administered by injection. Thiamine Injection is intended for veterinary use only.
What are the specific methods of Thiamine Hydrochloride administration in animals?
It is recommended parenteral administration via subcutaneous (SC) or intramuscular (IM) injection for cats, dogs, and horses. In cases of IM or SC administration, the application should be slow, and if the volume is bigger than 20ml, you should apply it to 2 separate places. This is the best way of application because it leads to minimal to no side effects.
Subcutaneous application includes lifting a flap of the loose skin and inserting a needle into the subcutaneous area. Avoid injecting near important vessels or nerves. Intramuscular injections lead to fast absorption because of the great blood supply. Check if the needle entered a blood vessel before administering the drug.
If administered intravenously (IV), Thiamine Hydrochloride Injection should be diluted with sodium chloride or glucose solution. It should be given to the animal as soon as possible when diluted. Intravenous administration might cause dose-dependent hemodynamic effects such as hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, ganglionic or neuromuscular blockade, apnea, or death. According to a study, IV administration at doses ≥ 20mg/kg (9.1mg/lb) to cats and 80mg/kg (36mg/lb) to dogs can lead to ganglionic and neuromuscular blockade.
Choose the method of thiamine hydrochloride administration based on the current animal health status. Be aware of the sterile and aseptic conditions when applying the drug. Clean the animal’s coat if it is very dirty when applying. Swab it with a high-quality skin antiseptic such as benzalkonium chloride in 70% alcohol, and never apply it to dirty or infected skin.
This supplement should only be used for lactating animals if recommended and administered by a veterinarian.
How should Thiamine Injection be stored?
This medication should be stored in a dark, dry location at temperatures under 30°C. The vial should be kept tightly sealed.
Dosage
How much Thiamine Injection should be given to horses?
The usual dose is 0.25ml per 45kg body weight. If the dosage is above 20ml, it should be divided and injected into two sites.
Follow the recommended advice for dosage because high intake can lead to the accumulation of vitamins in body tissues and fluids. This can cause toxicity and hypervitaminosis. A common sign is an increased urinary output.
Overdose of thiamine can block nerve transmission and lead to paralysis, restlessness, respiratory issues, convulsions, and cardiac problems. Thiamine can interfere with other B vitamins, the thyroid gland, and insulin.
Hypervitaminosis can be acute or chronic, with specific symptoms such as weakness, dizziness, nausea, tremor, diarrhea, or constipation. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should decrease the dose.
How much Thiamine Injection should be given to dogs?
The usual dose is 0.1-0.4ml per 45kg body weight. The dose can vary based on the stage of the deficiency.
How much Thiamine Injection should be given to cats?
The usual dose is 0.1-0.4ml per 45kg body weight. Cats are more susceptible to thiamine deficiency, so the dose can vary.
According to the National Research Council (NRC), the daily allowance for adult cats is 1.4mg of thiamine/1,000 kcal of metabolizable energy and 0.56mg of thiamine/1000 kcal of metabolizable energy.
Refer to a veterinary doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on dosage.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Thiamine Injection.
Some common side effects may include but are not limited to: • temporary irritation at injection site.
Serious side effects may include: • allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reactions
Some common side effects include mild reactions after intramuscular or subcutaneous application of thiamine hydrochloride.
For a comprehensive list of all possible side effects of this medication, consult a veterinarian.
Precautions
Do NOT use Thiamine Injection for an animal that: • has a known allergy or hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients.
Intramuscular and subcutaneous injections of Thiamine Injection might cause a mild inflammatory reaction at the application site in some animals.
This vitamin is safe during pregnancy, but higher doses might lead to side effects. It is also safe during lactation, but only the recommended amounts should be applied since the vitamin passes into the milk.
Thiamine hydrochloride injection can interact with other drugs and increase the risk of severe side effects. Ask the animal owners to describe the animal's medical history before applying the injection. The side effects due to this condition are not severe but can reduce the efficacy of the medication.
Thiamine administration can also change lab test results and might lead to false positive or false negative test results on certain parameters. Make sure to consult with colleagues before applying this drug and making any lab tests.
What are the most common animals Thiamine HCl Injection is used for?
Thiamine hydrochloride injections are primarily used to treat thiamine deficiency in animals and livestock. The specific common uses of thiamine hydrochloride injections include:
- Metabolism disorders and deficiencies
- Diseases in newborns
- Nutritional deficiencies of dogs and cats
- Lumbago of horses
- Cannibalism in chickens
- Secondary anemia and parasitic anemia
- Exhaustion
- Lack of appetite
- After birth malnutrition
Dogs' Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine hydrochloride treats thiamine deficiencies, lack of appetite, and nutritional deficiencies in newborns.
Horses' Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine hydrochloride is used to treat Lumbago in horses.
Cats' Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine hydrochloride is used to treat after-birth malnutrition, lack of appetite, metabolism disorders, and thiamine deficiencies.
Cows' Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine hydrochloride is used to treat thiamine deficiencies, metabolic disorders, and diseases in newborn cows.
Vitamin B1 injections are also indicated in cases of treating many diseases as a supportive medicine along with other drugs. Thiamine hydrochloride can improve the overall well-being of animals and is generally safe for all animals.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.