- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Lidocaine HCl Injection
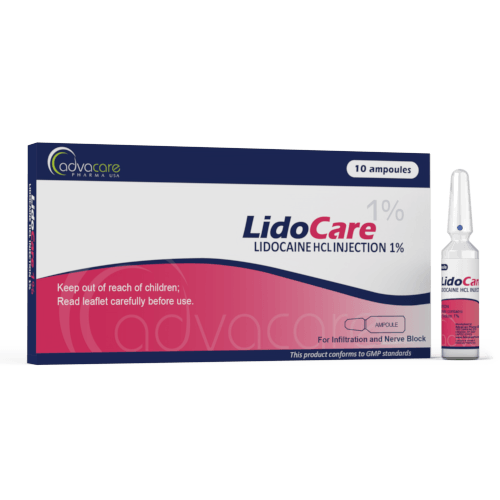
Lidocaine HCl Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Lidocaine HCl?
Active Ingredients: Lidocaine HCl
Lidocaine HCl Injection is used to numb an area of the body before surgery or an invasive medical procedure. It is is also given in an epidural (spinal block) to reduce the discomfort of contractions during labor. Lidocaine is sometimes used to treat ventricular arrhythmias if other treatment options are not available.
Lidocaine, also called by the name lignocaine, is classified as a local anesthetic. It works by blocking the nerve signals in the body. It stabilizes the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses. It has a local anesthetic action.
The medication is completely absorbed after parenteral administration but the rate of absorption depends. The site of administration and the presence or absence of a vasoconstrictor agent are factors that contribute to drug absorption. Intercostal nerve block causes the highest blood levels of lidocaine HCl, while subcutaneous administration results in the lowest levels. The plasma binding of lidocaine HCl depends on drug concentration, with a decrease in the fraction bound as the concentration rises. At concentrations ranging from 1 to 4 mcg of free base per mL, approximately 60 to 80 percent of lidocaine HCl becomes protein-bound. This binding is also influenced by the plasma concentration of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Lidocaine HCl crosses both the blood-brain and placental barriers, through passive diffusion.
Metabolism of lidocaine HCl occurs rapidly in the liver, with metabolites and unchanged drugs being excreted via the kidneys. Around 90% of administered lidocaine HCl is excreted in various metabolite forms, with less than 10% excreted unchanged. The primary metabolite found in urine is a conjugate of 4-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylaniline. The elimination half-life of lidocaine after an intravenous injection typically ranges from 1.5 to 2 hours. Due to the rapid metabolism of lidocaine HCl, any condition affecting liver function may alter its kinetics, which can double the half-life in patients with liver dysfunction. Renal dysfunction does not affect lidocaine HCl kinetics but may lead to increased accumulation of metabolites. Factors such as acidosis and the use of central nervous system (CNS) stimulants and depressants can influence the CNS levels of lidocaine HCl and limit its efficacy.
Lidocaine HCl Injection is available in 1% and 2% concentrations. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Lidocaine HCl s also available in a topical form as a cream.
AdvaCare Pharma is a global distributor and manufacturer of Lidocaine HCl Injections. This medicine is produced in our GMP-certified facilities in China, India, and the USA. Our factories are routinely inspected to ensure they meet the high standards necessary to comply with WHO guidelines and standards.
Why are we a leading Lidocaine manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma is a leading manufacturer of Lidocaine Injection. To ensure the quality of our manufactured pharmaceutical injection products, we adhere to stringent GMP guidelines at our manufacturing facilities. We partner with pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs, and government institutions across over 65 markets worldwide, and our track record over the past two decades demonstrates that AdvaCare Pharma is a reliable Lidocaine manufacturer and supplier dedicated to high-quality and efficacious medicines.
Uses
What is Lidocaine HCl used for?
It is used to induce localized numbness in patients before medical procedures.
How are Lidocaine HCl Injections used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution to be administered by injection. It is intended to be used for local infiltration anesthesia (percutaneous) or IV regional anesthesia (nerve block).
What dose should be given?
Adult Dosing Dosage may vary based on different medical indications:
- For local anesthesia, the maximum dose for infiltration is 4.5mg/kg. The maximum individual dose should not exceed 300mg.
- When used with epinephrine the dose should not exceed 7mg/kg (3.5 mg/lb) of body weight. The maximum total dose should not exceed 500mg.
- For a continuous epidural, there should be at least 90 minutes between each maximum dose.
- For continuous lumbar or caudal epidural anesthesia for non-obstetrical procedures, higher doses need to be administered to achieve adequate anesthesia.
- For a paracervical block in non-obstetrical patients the total administered amount should be 200mg.
- For IV regional, the recommended dose is 4mg/kg. The total dose should not exceed 300mg.
Children Dosing Recommended dosage for children may vary based on different medical conditions:
- For children over 3 years of age who have a normal lean body mass and normal body development, the maximum dose is determined by the child's age and weight.
- Children of 5 years who weigh 50 lbs, the recommended dose should not exceed 75-100mg (1.5 to 2mg/lb).
- Children need more dilute solutions (0.25 to 0.5%) of Lidocaine HCl. The total dosages should not exceed 3 mg/kg (1.4 mg/lb) for induction of intravenous regional anesthesia in children.
Renal Dosing There are no defined guidelines for patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Dosing There are no defined guidelines for patients with hepatic impairment.
The exact dose will vary due to factors such as the type of procedure, degree of anesthesia needed, and patient's condition. Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on dosage.
Who can use Lidocaine HCl?
Lidocaine HCl is mainly used as a local anesthetic to induce localized numbness. This drug can also be used for the acute management of ventricular arrhythmias occurring during cardiac manipulation such as cardiac surgery and life-threatening arrhythmias, particularly those that are ventricular in origin.
Special precautions should be taken when administering this drug to specific patient groups:
Pregnant Animal studies do not show any risks to the fetus caused by Lidocaine HCl. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. This drug should be applied with caution in pregnant women, especially during early pregnancy when maximum organogenesis occurs. Pregnant women should consult with their gynecologist before being treated with this drug. They should also inform their doctor if they are planning to get pregnant soon if the doctors plan to administer this injection.
Nursing There is no evidence that this drug is excreted in human milk. Special caution should be considered when administering this drug to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Children should receive lower doses according to their age, body weight, and physical condition.
Labor and Delivery This is a local anesthetic that can rapidly cross the placenta when used for epidural, paracervical, pudendal, or caudal block anesthesia. There are risks for maternal, fetal, and neonatal toxicity. The potential toxicity depends on the procedure, the amount of the drug, and the technique of administration. Some side effects like alteration of the CNS, peripheral vascular tone, and cardiac function might occur.
Regional anesthesia with Lidocaine HCl might cause maternal hypotension. When this occurs, the patient’s legs need to be elevated and the patient needs to be positioned on the left side which will prevent hypotension.
Anesthesia during labor and delivery can affect the forces of childbirth by altering uterine contractility or maternal expulsive efforts. Paracervical block anesthesia might lead to a shorter duration of the first stage of labor and easier cervical dilation, while spinal and epidural anesthesia may prolong the second stage by reducing the urge to bear down or interfering with motor function. This can potentially increase the need for forceps assistance.
This injection may temporarily weaken muscle strength and tone in newborns. Fetal bradycardia can also occur under paracervical anesthesia. Monitoring fetal heart rate is essential while using this medication during labor, especially in cases of prematurity, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, or fetal distress.
Doctors should adhere to recommended dosages and also should be careful about unintended injection of the drug into blood vessels or the fetal brain. Neonatal depression and seizures are common for such cases and this condition requires intervention and supportive care.
Other warnings
This injection should be given only by clinicians and nurses. Other medical professionals trained in administering this drug can also do it.
Patients should inform their doctors about any drugs they are taking at the moment and about their current health status.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Lidocaine HCl Injection.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- swelling near the injection site
- dizziness
- nausea
Serious side effects may include: • signs of an allergic reaction
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or you notice any other symptoms, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Lidocaine HCl Injection if:
- You are allergic to lidocaine or any other ingredients.
- You are allergic to other local anesthetics.
- You are receiving treatment concurrently with class I antiarrhythmic agents (quinine, flecainide, disopyramide, or procainamide).
- You have Stokes-Adams syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or cardiac block without a pacemaker.
- You have used amiodarone hydrochloride in the past.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.
Patients should be informed in advance of the temporary loss of sensation and motor activity that they may experience after administration of this medication.
Lidocaine might lead to methemoglobinemia and it has to be treated as soon as possible.
If the patients experience any side effects, they should inform their doctors as soon as possible.
The vital signs of the patient need to be monitored when this drug is given.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions.
This drug should be kept out of reach of children and pets.
References
Double-blinded comparison of diphenhydramine versus lidocaine as a local anesthetic
The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy, onset of action, duration of action, and side effects of 1% diphenhydramine compared with 1% lidocaine when used as a local anesthetic agent.
It was a prospective, double-blinded, cross-over study that included 10 healthy male volunteers, aged 26 to 38 years old.
The results revealed that there were no significant changes in mean pinprick sensation observed from baseline to 30 minutes. Changes were noted at 45 minutes (P = 0.36) and 60 minutes (P = 0.036). Lidocaine demonstrated a longer duration of effective anesthesia compared to diphenhydramine (81 minutes versus 42 minutes, P = 0.028). One participant experienced skin necrosis at the injection site following diphenhydramine administration.
The study concluded that 1% lidocaine yielded longer-lasting local anesthesia and the depth of anesthesia was significantly higher 30 minutes after administration compared to diphenhydramine.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.