- Home›
- Pharmaceuticals›
- Injections›
- Small Volume Injections›
- Progesterone Injection
Progesterone Injection
Dosage
Packaging
What is Progesterone?
Active Ingredients: Progesterone
Progesterone Injection is a drug used to replace the hormone progesterone when the body does not make enough of it. It is typically used for amenorrhea in women who are not pregnant or have gone through menopause. Progesterone is also used to treat abdominal uterine bleeding caused by low hormone levels.
Progesterone Injections are also commonly used in fertility treatments in order to support reproductive health and pregnancy. For in vitro fertilization (IVF), these shots are typically administered during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle to help increase the chances of a successful embryo implantation.
Progesterone is an endogenous steroid and sex hormone which is primarily produced by the ovaries, though it is also produced in smaller amounts by the adrenal glands in both men and women. This hormone intervenes in many physiological functions and is vital for regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining the uterine lining. Insufficient production of this hormone in the body can lead to menstrual irregularities and symptoms resembling those of menopause in women.
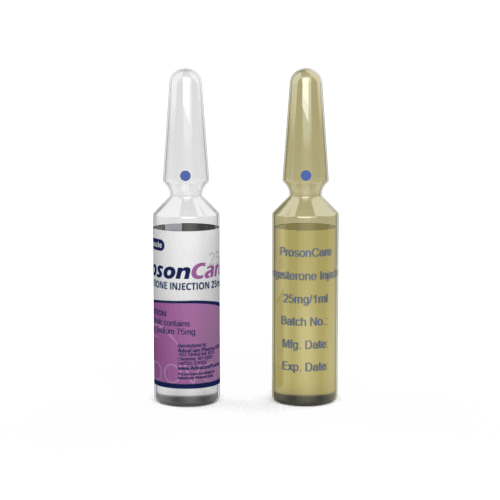
Progesterone Injection has been produced as a sterile solution which has been contained in an ampoule. It is available in two dosages: 25mg/ml or 50mg/ml. These ampoules are packaged as a box of 10 or 100 pieces. Injections of progesterone are intended for intramuscular use.
AdvaCare is a GMP-certified producer of Progesterone Injection. This medication is manufactured in our factories in China, India, and the USA. We routinely inspect these facilities to ensure our products meet quality and safety standards.
Why are we a leading Progesterone manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma, a US-owned pharmaceutical company, is a manufacturer of Progesterone Injection with GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities located worldwide. We conduct frequent GMP, third-party and internal facility inspections to ensure that our manufactured injectable treatments exceed the stringent requirements of importing countries and our distributors.
As a renown Progesterone manufacturer and global supplier of 120+ pharmaceutical injection products, our global reach extends to over 65 markets ensuring that pharmaceutical distributors, hospitals, pharmacies, NGOs and government institutions receive the quality-assured treatments they need.
Uses
What is Progesterone used for?
It is used to treat amenorrhea or functional uterine bleeding that is associated with progesterone deficiency in the absence of organic pathology (such as submucous fibroids or uterine cancer). Injections of progesterone are used during fertility treatments to support the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and to help prepare the uterine lining for embryo implantation during in vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
How are Progesterone Injections used?
This medication is manufactured as a solution intended for intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. It is typically administered in a hospital or clinic setting, though there have been instances where a patient may need to self-administer in the home environment.
Before use, the solution within the ampoule should be carefully inspected for any visual particles or discoloration. The medication should be discarded if any visual changes have been observed or if it is after the printed expiration date.
Prior to the injection, the injection site should first be cleaned with rubbing alcohol. Unlike other steroid injections, progesterone is known to cause irritation at the site of injection, so it may be necessary to apply lidocaine or another numbing agent. It is important to note that the location of the injection site should change daily in order to avoid any complications.
How should Progesterone Injections be stored?
It is recommended to store any unused ampoules of progesterone at room temperature between 20-25°C. The medicine should be kept out of heat or excessive light.
What dose should be given?
Recommended dosage guidelines may vary depending on medical condition:
- For the treatment of amenorrhea, the usual dose is 5-10mg, given once a day, IM. The duration of treatment is 6-8 days. When ovarian activity sufficiently produces a proliferative endometrium, withdrawal bleeding typically occurs 48-72 hours after the last injection. Normal cycles may return without the need for additional medical intervention.
- For uterine bleeding associated with hormonal imbalance, the usual dose is 5-10mg, given once a day, IM, for 6 doses. Bleeding should stop within 6 days. If estrogen is also being given, therapy with progesterone should begin two weeks after starting estrogen. Treatment should be discontinued if menstrual flow begins. If menstrual flow begins during the course, stop the treatment.
- For luteal-phase support during IVF and ART, the usual dose is 25-50mg given once per day, IM.
Refer to a doctor or pharmacist for guidelines on the exact dosage.
Who can use Progesterone?
Progesterone Injections can be administered to postmenarcheal females who are not pregnant and have not gone through menopause. Caution is advised for specific groups of patients.
Pregnant This medication should not be administered to pregnant women, particularly in the first trimester. Animal studies have indicated a wide range of genital abnormalities in the fetus during gestation. An effective form of birth control should be used during treatment with this medicine.
Breastfeeding Progesterone is known to be excreted into milk. Benefits must be weighed against the risks before recommending therapy with progesterone. There is not enough human data to establish the safety of nursing mothers. There have been reports of decreased milk production, though the data is limited.
Children The safety and effectiveness have not been established for pediatric patients.
Geriatric The safety and effectiveness have not been established for elderly patients over the age of 65.
Other warnings
For patients with renal impairment, caution and careful monitoring are recommended, as progesterone metabolites are excreted primarily by the kidneys. The safety and effectiveness have not been established for this population.
For patients with hepatic impairment, Progesterone Injection is contraindicated in patients with liver disease or dysfunction, as progesterone is metabolized by the liver.
For patients with a history of depression, treatment should be discontinued if a major episode recurs.
There has been reported a decrease in glucose tolerance in some patients who are undergoing combination therapy with estrogen and progestin. It is recommended to carefully observe diabetic patients undergoing treatment with progesterone.
This drug may impact carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The dose may be reduced for at-risk populations.
Progesterone is associated with fluid retention, so it is recommended to carefully consider and observe patients with conditions affected by fluid retention, such as epilepsy, migraines, asthma, cardiac disease, or renal dysfunction.
It is important to note that progesterone should not be used to test for pregnancy nor is it effective in preventing miscarriage.
Side Effects
As with all pharmaceuticals, some unwanted effects can occur from the use of Progesterone Injection.
Progesterone can influence mood. Some individuals may experience mood changes or irritability as a side effect of progesterone supplementation.
Common side effects include, but may not be limited to:
- pain or swelling at the site of injection
- breast tenderness
- headache
- changes in weight
- acne
- nausea
- hair loss (scalp)
- increased body hair
- drowsiness
- dizziness
Serious reactions that may require medical attention include the following:
- unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge
- nausea or vomiting that does not stop
- a change in menstrual periods
- breast lumps
- changes in mood or mental condition
- signs of jaundice (e.g. frequent or painful urination, dark urine, yellowing skin or eyes, abdominal pain)
- allergic reaction
When used with an estrogen product, progesterone may cause some rare but serious complications due to blood clots. Seek medical attention immediately if the following symptoms appears:
- pain in the chest, jaw, or left arm
- weakness on one side of the body
- difficult speaking
- blurry vision, loss of vision, or other vision changes
- confusion
- trouble breathing
- a sudden severe headache
- fainting
For a comprehensive understanding of all potential side effects, consult a medical professional.
If any symptoms persist or worsen, or any new symptoms appear, please call your doctor.
Precautions
Do NOT use Progesterone Injection if:
- You are allergic or hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- You have or have had thrombophlebitis or cerebral apoplexy.
- You have liver disease.
- You have a known or suspected malignancy of the breast or genital organs.
- You have vaginal bleeding that is undiagnosed.
- You have a missed abortion.
Before treatment, consult your doctor regarding any medications you are taking to address potential drug interactions.Some drugs known to interact include azole antifungals (e.g. ketoconazole), rifamycins (e.g. rifabutin), anticonvulsants (e.g. carbamazepine, phenytoin), or herbal supplements like St. John's wort.
This medication may not be suitable for people with certain conditions, so it is important to consult with a doctor if you have any health conditions, particularly a history of blood clots, bleeding in the brain, liver disease, cancer, unknown vaginal bleeding, migraines, seizures, cardiovascular disease, asthma, kidney disease, depression, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
Do not use this medication while pregnant or breastfeeding. It is particularly important to not use this medicine during the first 4 months of pregnancy, as it may harm the fetus. Consult a doctor or healthcare professional before treatment.
This medication may cause dizziness or drowsiness as a side effect, so driving or operating machinery should be avoided until the effects have passed. Limit or do not drink alcohol while undergoing treatment, as alcohol may increase these adverse effects.
Progesterone treatment has been associated with melasma (dark spots on the skin), which may worsen when exposed to sunlight. It is recommended to wear protective clothing when outside and to avoid sun lamps and tanning beds.
Some laboratory tests may be affected by recent treatment with progesterone, and it is important to inform any laboratory staff of recent treatment.
References
The effect of progesterone in adolescent girls and young women with functional uterine bleeding
This study contains a detailed menstrual record of 24 adolescent girls and young women with functional uterine bleeding.
These patients received progesterone or anhydrohydroxy progesterone, and the effect on the menstrual pattern was observed over a period of many months in most cases.
The conclusion is that in about one-third of the observations, normal cycles occurred for four months or more after therapy.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.